News and Events Archive
All stories that have been tagged with Publications
New publication from Krishna in Nature Nanotechnology
Publications

In his latest publication, Krishna characterized how cortical neurons sense and respond to various mechanical stimuli. The cover image of Krishna’s work depicts a colored scanning electron microscopy (SEM) image of a network of cortical neurons grown on a microelectrode array used for combined force and electrophysiological measurements.
In mitosis integrins reduce adhesion to extracellular matrix and strengthen adhesion to adjacent cells
Publications
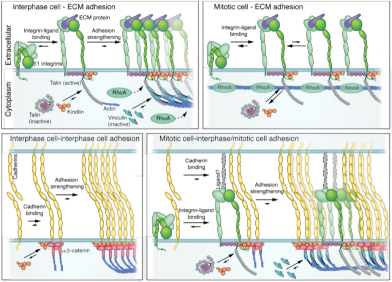
How cells modulate their adhesion to the extracellular matrix (ECM) and to neighboring cells during mitotic cell rounding remained elusive. We recently deciphered that cell-ECM adhesion components are released prior to mitosis and are rewired to synergize with cadherins to strengthen adhesion to adjacent cells.
How cells initially sense and adhere to fibrillar extracellular matrices
Publications
So far, it has remained elusive how cells initially sense and respond to fibrillar extracellular matrices during adhesion initiation and how this initial sensing continuously influences cell behavior. In our recent paper published in Advanced Science, we engineered biomimetic fibrillar fibronectin matrices using 3D-printed microgrids and simple solution shearing.
Under control to the very end – how our cells kill themselves
Publications
Until recently, it was assumed that cells simply burst and die at the end of their life. Now, a team of researches at the Biozentrum, University of Basel, the University of Lausanne and our group (Stefania Mari and group alumna Kristyna Pluhackova) have provided new insights into the final step of cell death.
Focused-ion beam modification of microcantilevers allows to tailor their mass sensitivity to monitor single adherent living cells.
Publications

The results of this study from our group have been published in Nano Letters.
Substrate-binding changes the mechanical stability of the sugar transporter MelB
Publications
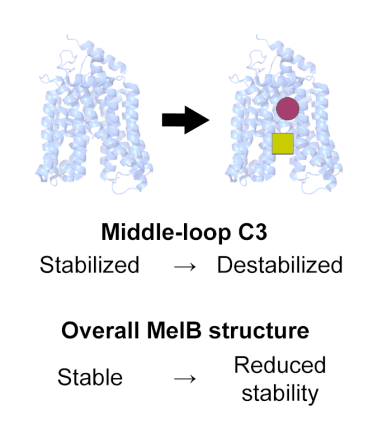
The results of the collaborative research project between our group and the Guan lab from Texas Tech University have been published in Structure.
Polymyxin antibiotics disrupt the integrity of bacterial outer membrane by forming crystalline structures
Publications
The results of our collaborative research project with Prof. Sebastian Hiller’s Lab from Biozentrum, University of Basel, have been published in Nature Communications.
A cholesterol analog stabilizes basally active conformations of the β2-adrenergic receptor
Publications

The latest work of Tetiana Serdiuk and colleagues from our laboratory has been published in Science Signaling.
Cells on the run!
Publications
Many cells in the body must pass through tissues, which sometimes requires them to get out of tight corners. An international research project co-led by the Muller group has now examined how cells recognise and escape from such bottlenecks. Among the results of the team’s work are new pointers for how to improve immunotherapy.
GPCRs, integrins and cell adhesion
Publications
The correct regulation of adhesive interactions between cells and their environment is essential for health. Our latest paper in Nature Materials provides mechanistic insights as to how extracellular signals are transmitted into the cell where they lead to intracellular regulation of cell adhesive properties to the extracellular matrix. The process is important for tissue formation and wound healing while its dysregulation may result in cancer progression.
Neuron mechanics
Publications
How do the different parts of a neuron respond to mechanical stimuli such as those occurring during subtraumatic forces? In an interdisciplinary effort with the Fussenegger group at D-BSSE and the Roska group from the Institute of Ophthalmology (IOB) of the University Basel, we investigated the mechanosensitivity of neurons from the rat brain. The findings may guide future studies to mechanically control neurons by, for example, electromagnetic forces or ultrasound.
Mechanobiology!
Publications

Enjoy our newest review in the first issue of Nature Reviews Physics. The review, co-written by young scientists Michael, Gotthold, David & Benjamin (& some older ones), describes how AFM-based approaches can contribute to address pertinent problems in mechanobiology at the crossroads of medicine, biology, biophysics and engineering. It describes how the responses of proteins, cells, tissues and organs to mechanical cues contribute to development, differentiation, physiology and disease.
Punching holes in membranes!
Publications

Using time‐lapse AFM at high temporal and spatial resolution, Estafania Mulvihill unravelled the mechanisms of how gasdermin-D assembles and forms pores in lipid membranes. Dynamic structures of arc‐ and slit‐shaped protein oligomers that transform into larger thermodynamically stable ring‐shaped oligomers were observed. The insights highlight the mechanism by which gasdermin-D self‐assembles and forms transmembrane pores.
Virus stamping!
Publications

During the past few years Rajib Schubert and colleagues have developed a new and efficient and very simple method to target virus transfection. Basically it guides the virus (electro)mechanically to single cells or cellular regions in vitro and in vivo. The method was published as cover story in Nature Biotechnology.
Genome-scale mechanical phenotyping of mitotic cells
Publications
To divide, most animal cells drastically change shape and round up against extracellular confinement. Here, we phenotype the contribution of > 1000 genes to the rounding of single mitotic cells against confinement. Our screen identifies 49 genes relevant for mitotic rounding. Among these being disease related including Parkinson's.
Integrins sense load and signal to reinforce adhesion in less than 1 s
Publications
During adhesion initiation, fibroblasts respond to mechanical load by strengthening integrin-mediated adhesion to fibronectin (FN) in a biphasic manner. This unique, biphasic cellular adhesion response is mediated by α5β1 integrins, which form catch bonds with FN and signal to FN-binding integrins to reinforce cell adhesion much before visible adhesion clusters are formed..
How much does life weigh?
Publications

Our research and engineering team has developed a scale for measuring the total mass of life mammalian cells. It allows the weight of individual living cells, and any changes in this weight, to be determined quickly and accurately for the first time. The invention, which arises significant interest both in and outside the field of biology has been published in Nature.
New Paper in Nature Nanotechnology!
Publications
In this paper we review together with our scientific colleagues the AFM as an nanotechnological platform that allows biological samples, from single molecules to living cells, to be visualized and manipulated. We review the basic principles, advantages and limitations of the most common AFM bioimaging modes, including the popular contact and dynamic modes, as well as recently developed modes such as multiparametric, molecular recognition, multifrequency and high-speed imaging.
New Paper in Nature Reviews Materials
Publications
In this Review written with our colleagues, we survey basic and advanced AFM-related approaches and evaluate their unique advantages and limitations in imaging, sensing, parameterizing and designing biointerfaces. We anticipate that in the next decade these AFM-related techniques will show a strong influence on the way researchers view, characterize and construct biointerfaces, thereby helping to solve and address fundamental challenges that cannot be addressed with other techniques.
New Paper in Nature Communications
Publications
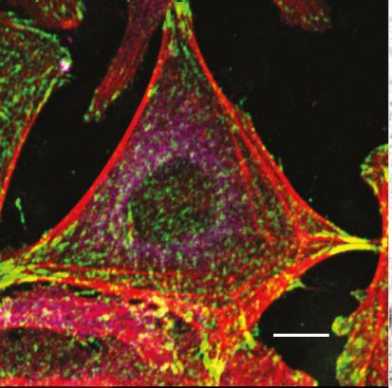
In our new paper we find that upon initiating cell adhesion αV-class integrins engaged to the extracellular matrix protein, fibronectin, signal to α5β1 integrins to establish additional adhesion sites and to strengthen cell adhesion. The cooperative crosstalk between both fibronectin-binding integrin classes towards establishing cell adhesion appears to be a basic cellular mechanism. See Bharadwaj et al Nat. Commun.
New Paper in Nature Nanotechnology!
Publications
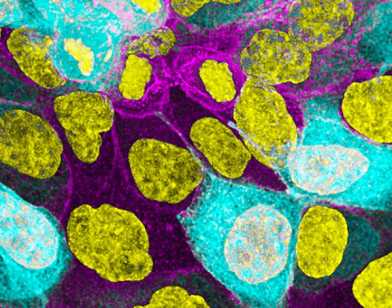
Viral infection is initiated when a virus binds to cell surface receptors. However, the very first binding events of enveloped viruses are hardy understood. Here, we introduce an nanoscopic assay to image animal cells and to detect virus-binding events within the first ms of contact at high resolution. We observe how viruses quickly occupy binding sites of the viral glycoprotein to initiate virus fusion and uptake. See Alsteens et al. Nat. Nanotech. (2016)
New Paper in Nature Chemical Biology
Publications
Congrats to Tania. Her newest paper, appearing in Nature Chemical Biology, describes how the chaperone/translocase YidC supports the insertion and folding of the sugar transporter lactose permease LacY. YidC prevents the LacY polypeptide from misfolding and supports the stochastic and stepwise insertion and folding of structural segments until the folding of native LacY has been completed. The work was done together with Ron Kaback UCLA.
New paper in Nature Cell Biology
Publications
Congrats to Moritz to his new paper appearing in Nature Cell Biology. In collaboration with the Steinmetz group (PSI Villigen, Switzerland), Moritz applied high-resolution AFM to image engineered SAS-6-based oligomers with symmetries ranging from five- to ten-fold. SAS-6 proteins are thought to assemble an about nine-fold symmetric cartwheel structure which are important for centrioles to form centrosomes in eucaryotes. See M. Hilbert et al. Nature Cell Biology (2016) 18, 393-403.
New paper in Nature Communications
- Publications
- News
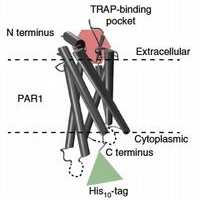
Congrats to Moritz and David to their new paper appearing in Nature Communications. David and Moritz developed a high-resolution method that allows to image single G-protein coupled receptors and to simultaneously detect their binding to two different ligands. The work was done in collaboration with Brian Kobilka (Stanford) and Shaun Coughlin (UCSF).
New paper in Nature Communications
- Publications
- News
Congrats to Barbara on her new paper appearing in Nature Communications. Barbara developed together with the group of Andreas Hierlemann a micropillar assay that mimics the mechanical properties of the epithelia.
New paper in PNAS
- Publications
- News
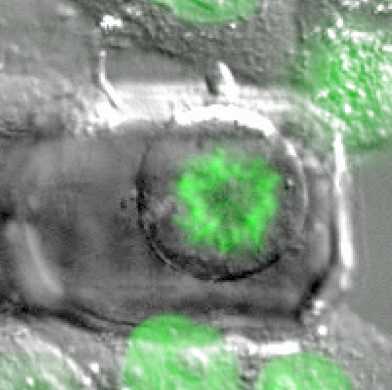
Congrats to Cedrics new paper appearing in PNAS. Cedric found ways to mechanically control mitotic progression in animal mitotic cells.
New paper in Nature Structural & Molecular Biology
- Publications
- News
Congrats to Yosh to his new paper appearing in Nature Structural & Molecular Biology. Yosh together with the group of Sebastian Hiller (Biozentrum, University of Basel) developed a new nanotechnological assay to study the chaperone assisted folding of integral beta-barrel proteins. By combining this assay with NMR spectroscopy it became possible to unravel the mechanisms of how periplasmic chaperones assist the folding of outer membrane proteins into lipid membranes.
New paper in Nature Methods
- Publications
- News
Congrats to David and Moritz to their new paper appearing in Nature Methods. David and Moritz developed a high-resolution method that allows to image single G-protein coupled receptors and to simultaneously detect their free-energy landscape of ligand binding. The work was done in collaboration with Brian Kobilka (Stanford) and Shaun Coughlin (UCSF).