ERC Advanced Grant "NeuroCMOS"
Seamless Integration of neurons with CMOS microelectronics ("NeuroCMOS")

The ERC Advanced Grant NeuroCMOS (external page Grant Agreement Nº 267351) included to seamlessly integrate state-of–the-art microelectronics and living neuronal cells in a comprehensive and interdisciplinary approach to advance the understanding of neuronal behavior. The project included the development of a novel multifunctional microelectronics chip platform in complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) technology, which served to enable research on network dynamics and plasticity of neuronal networks in various preparations (brain slices, dissociated cells, retinae), and the necessary concurrent development of algorithms to efficiently process and harness the information in the obtained data.
The grant started on June 1st, 2011 and ended on May 31st, 2016.
An ERC proof-of-concept (PoC) project "Multi-well High-resolution Electrophysiology Platform" (MwHresEP, external page Grant Agreement N° 755383) has been executed between June 1st, 2017 and November 30th, 2018. The purpose of this ERC-PoC-project was to commercialize the developed CMOS-based chip technology and software for neuroscientific research and industrial use in drug discovery and development in collaboration with the spin-off company external page MaxWell Biosystems, which was founded after and with the results of the NeuroCMOS project.
Relevant Publications
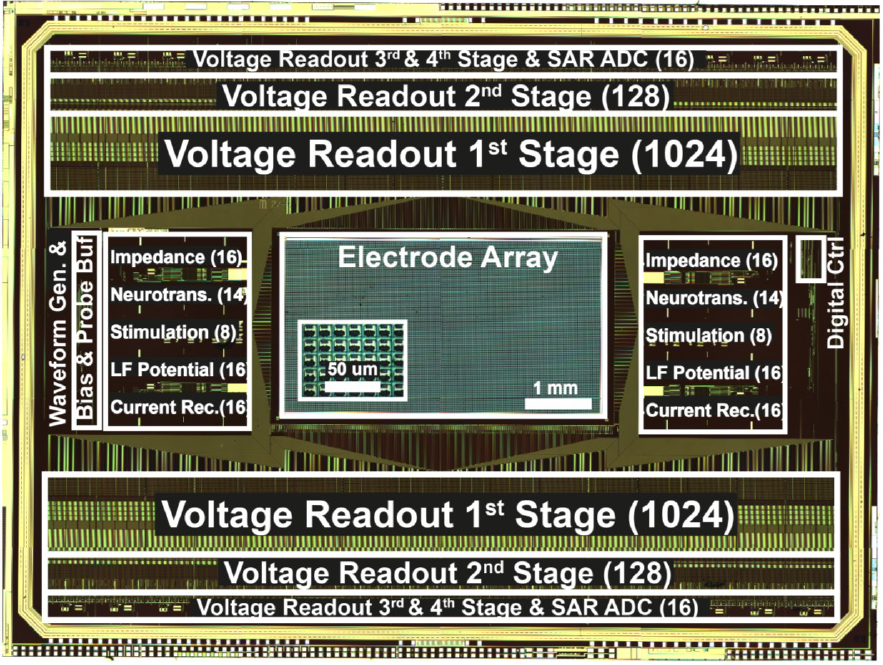
J. Dragas, V. Viswam, A. Shadmani, Y. Chen, R. Bounik, A. Stettler, M. Radivojevic, S. Geissler, M. Engelene J. Obien, J. Müller, A. Hierlemann, "In-vitro multi-functional microelectrode array featuring 59760 electrodes, 2048 electrophysiology channels, stimulation, impedance measurement and neurotransmitter detection channels", IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2017, Volume 52 (6), in print (DOI:10.1109/JSSC.2017.2686580). external page Online
D. Jäckel, D. J. Bakkum, T. L. Russell, J. Müller, M. Radivojevic, U. Frey, F. Franke & A. Hierlemann, "Combination of high-density microelectrode array and patch clamp recordings to enable studies of multisynaptic integration", Scientific Reports 2017, Vol. 7, Art. No. 978 (DOI:10.1038/s41598-017-00981-4). external page Online
W. Gong, J. Senčar, D.J. Bakkum, D. Jäckel, M. Engelene J. Obien, M. Radivojevic, and A. Hierlemann, "Multiple single-unit long-term tracking on organotypic hippocampal slices using high-density microelectrode arrays", Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10:537 (DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2016.00537). external page Online
M. Radivojevic, D. Jäckel, M. Altermatt, J. Müller, V. Viswam, A. Hierlemann, D. Bakkum, "Electrical identification and selective microstimulation of neuronal compartments based on features of extracellular action potentials", Scientific Reports 2016, 6, 31332 (DOI:10.1038/srep31332). external page Online
K. Yonehara, M. Fiscella, A. Drinnenberg, F. Esposti, S. Trenholm, J. Krol, F. Franke, B. Gross-Scherf, A. Kusnyerik, J. Müller, A. Szabo, J. Jüttner, F. Cordoba, A. P. Reddy, J. Németh, Z. Nagy, F. Munier, A. Hierlemann, B. Roska, "Congenital nystagmus gene FRMD7 is necessary for establishing a neuronal circuit asymmetry for direction selectivity", Neuron, 2016, 89(1), pp. 177-193 (DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.11.032). external page Online / external page Video abstract
M. K. Lewandowska, M. Radivojević, D. Jäckel, J. Müller, and A. Hierlemann, "Cortical axons, isolated in channels, display activity-dependent signal modulation as a result of targeted stimulation", Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10:83 (DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2016.00083). external page Online
J. Dragas, D. Jaeckel, A. Hierlemann, F. Franke, "Complexity Optimisation and High-Throughput Low-Latency Hardware Implementation of a Multi-Electrode Spike-Sorting Algorithm", IEEE Trans. On Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2015, 23(2), pp. 149-158 (DOI: 10.1109/TNSRE.2014.2370510). Online
M. K. Lewandowska, D. J. Bakkum, S. B. Rompani, A. Hierlemann, "Recording Large Extracellular Spikes in Microchannels along Many Axonal Sites from Individual Neurons", PLoS ONE, 2015, 10(3): e0118514 (DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118514). external page Online
J. Müller, M. Ballini, P. Livi, Y. Chen, M. Radivojevic, A. Shadmani, V. Viswam, I. L. Jones, M. Fiscella, R. Diggelmann, A. Stettler, U. Frey, D. J. Bakkum, A. Hierlemann, "High-resolution CMOS MEA platform to study neurons at subcellular, cellular, and network levels", Lab Chip, 2015, 15, pp. 2767-2780 (DOI: 10.1039/C5LC00133A). external page Online
Douglas J. Bakkum, Urs Frey, Milos Radivojevic, Thomas L. Russell, Jan Müller, Michele Fiscella, Hirokazu Takahashi, Andreas Hierlemann. "Tracking axonal action potential propagation on a high-density microelectrode array across hundreds of sites", Nature Communications 2013, 4:2181 (DOI: 10.1038/ncomms3181). external page Online