Article on detection of individual axonal action potentials in "eLIFE"
Article by Milos Radivojevic, Felix Franke et al. on "Tracking individual action potentials throughout mammalian axonal arbors" published in journal eLIFE.

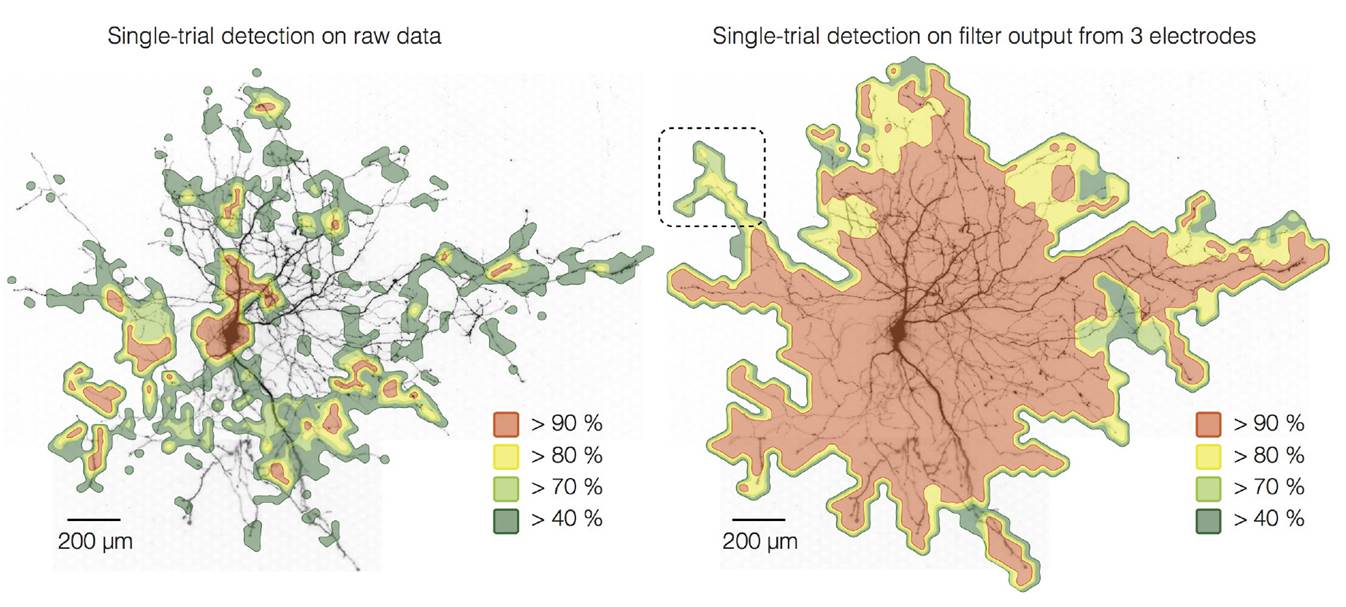
A new article by Milos Radivojevic and other BEL authors, entitled "Tracking individual action potentials throughout mammalian axonal arbors" was published in the journal eLIFE. By means of high-density microelectrode arrays, the authors tracked the propagation of action potentials through heavily arborized axonal trees of cultured mammalian cortical neurons. They showed that pulse-to-pulse variability in propagation speed was rather low, although the variability increased with increasing spike rate, and that branch-point failures were absent. The acquired data bear on spike-timing plasticity and on computational models that utilize coincident activation, such as synfire chains.
external page eLIFE publishes important research in all areas of the life and biomedical sciences. The research is selected and evaluated by working scientists and is made freely available to all readers without delay. eLife also invests in open-source tool development to accelerate research communication and discovery.