Watching micro-tissues grow, communicate and die
New paper in Advanced Biosystems on immobilizing micro-tissues in hydrogel drops for 3D imaging with two-photon microscopy.

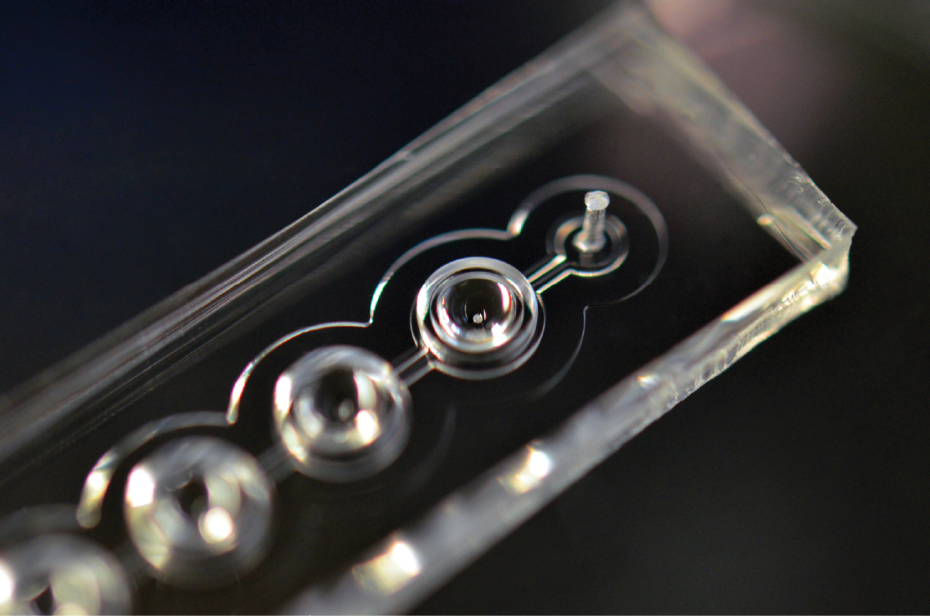
The article by Elise Aeby, Patrick Misun and Olivier Frey in Advanced Biosystems, titled "Microfluidic Hydrogel Hanging-Drop Network for Long-Term Culturing of 3D Microtissues and Simultaneous High-Resolution Imaging", presents a versatile microfluidic platform for long-term culturing and analysis of 3D microtissues. The platform is compatible with time-lapse high-resolution confocal microscopy. Hanging hydrogel drops enable the precise placement and stable immobilization of the microtissues in the microfluidic chip. The chip includes perfusion capability to apply drugs, staining and clearing solutions. The features of the chip are demonstrated by studying (i) colon cancer microtissues to monitor tissue growth and cell death; on-chip clearing was used to augment the penetration depth for endpoint imaging; (ii) primary human liver microtissues were exposed to cytochalasin D to observe its effect on the bile canaliculi.
An image of the paper also was selected for the backside cover of the journal.
external page Advanced Biosystems is publishing research into technologies that enhance and harness biological systems, including systems and synthetic biology, advanced therapeutics, and biohybrids and neurotechnology.