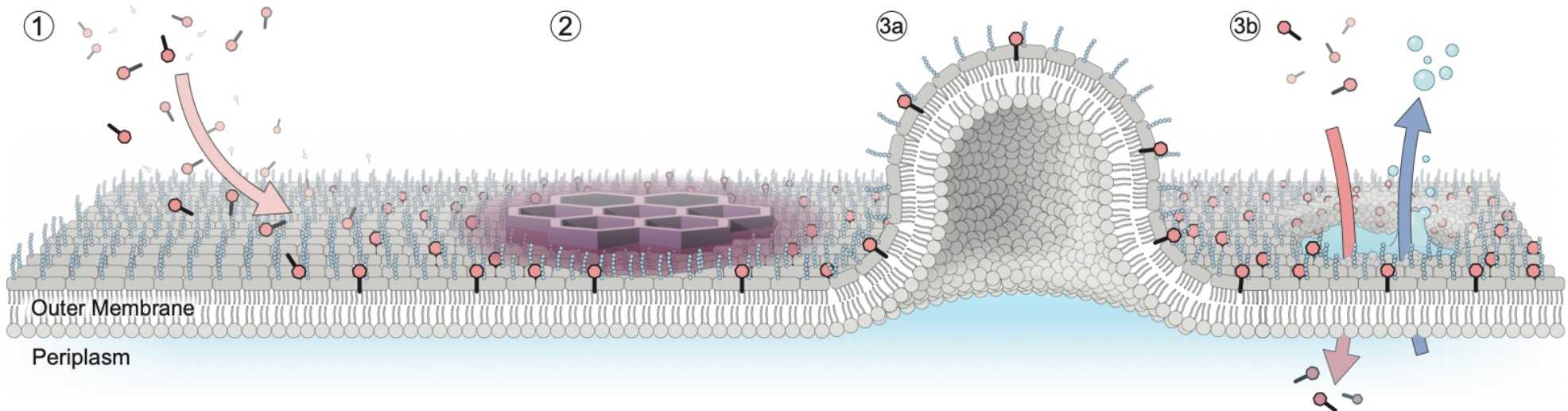
Last-resort antibiotics prepare E. coli membranes for disruption
Polymyxins are considered last-resort antibiotics which are still effective against multi-drug resistant pathogens. In a study published by Nature Communications, Selen Manioglu and colleagues from the Biophysics group and the Biozentrum, University of Basel, now describe their mechanistic effect at the molecular level. Using atomic force microscopy imaging, the results show that Polymyxins bond to membrane lipids and the newly formed crystalline structure weakens the membrane until it bursts.
Find original publication:
Manioglu, S, S M Modaresi, N Ritzmann, J Thoma, S A Overall, A Harms, G Pert, A Luther, A B Barnes, D Obrecht, D J Müller, and S Hiller (2022) external page Antibiotic polymyxin arranges lipopolysaccharide into crystalline structures to solidify the bacterial membrane. Nature Communications, 13 (6195), https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-33838-0
Commentary on this article:
Paiva, T O, A Viljoen, and Y F Dufrêne (2022) Sexternal page eeing the unseen: High-resolution AFM imaging captures antibiotic action in bacterial membranes. Nature Communications, 13 (6196), https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-33839-z
Learn about the Biophyics group led by Daniel J Müller.